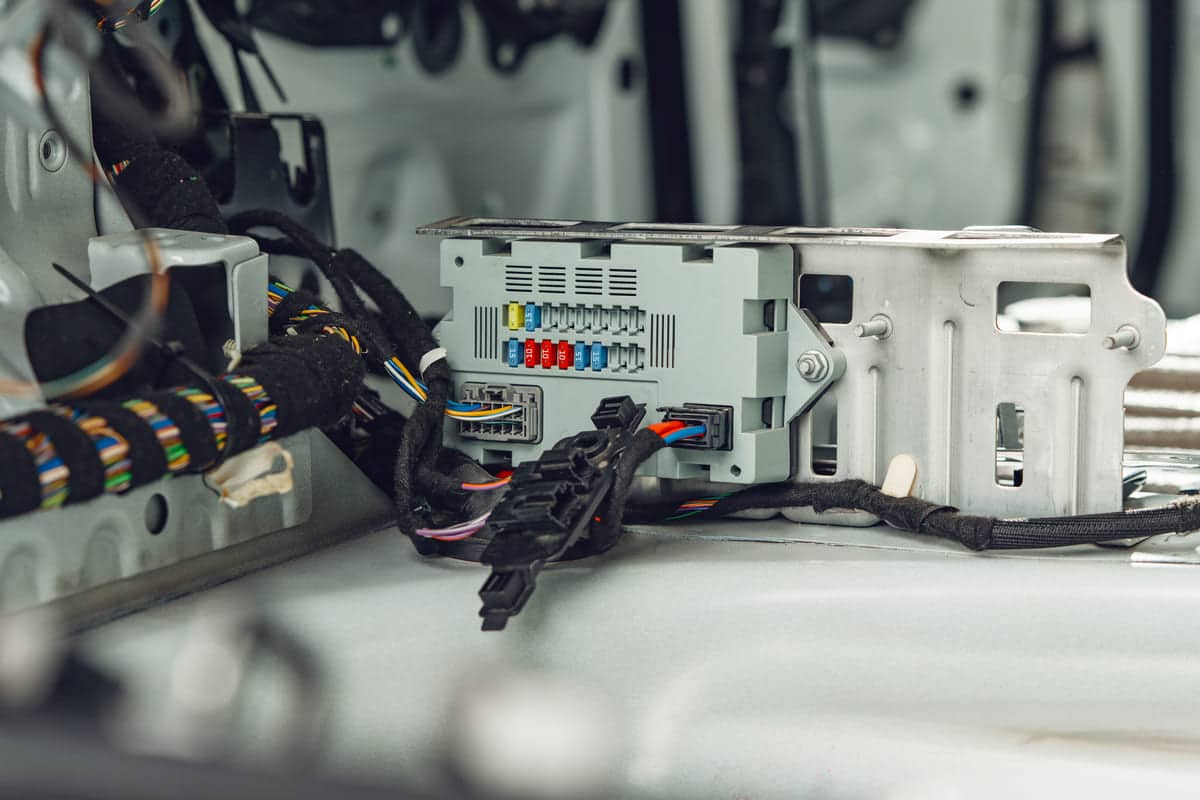
An electronic control unit integrates with the vehicle architecture and makes real-time adjustments. These units are key to management, transmission control, and other critical vehicle systems, and contribute to overall vehicle performance.
What Is an Electronic Control Unit?
An electronic control unit also known as ECU is a small device in a vehicle that controls a function. Modern vehicles have over 100 ECUs. These ECUs control things like engine and power steering control, and comfort features like power windows and HVAC.
They also control security features like door locks and keyless entry, and features like airbags and auto brakes. Each ECU has its own chip running its software and needs power and data connections.
Electronic control units get inputs from different parts of the vehicle depending on their function. For example, a door lock ECU gets input from the door lock button or a key fob. An ECU gets data from crash and seat sensors. An auto brake ECU uses radar to detect obstacles.
Based on these inputs the ECU sends commands to actuators to perform actions. For example the door lock ECU activates an actuator to lock or unlock doors. The airbag ECU decides which airbags to deploy based on passenger location. The auto brake ECU brakes to avoid a collision.
As vehicles get more features space for electronic control unit becomes limited. Each new feature requires its own ECU so space and efficiency become a challenge for manufacturers.
References
- Electronic control unit. Wikipedia. Retrieved from on 08 August 2024
- Electronic Control Unit. ScienceDirect. Retrieved from on 08 August 2024
What are the Types Of ECUs?
Electronic control units (ECUs) come in different types, each controlling a function in a vehicle. Here are some common types and their roles:
Engine Control Module (ECM)
The ECM is the brain of the engine. It controls fuel injection, , and air-fuel mixture to make the engine run smoothly and efficiently. The ECM also monitors sensors for temperature, pressure, and other data to optimize performance and reduce emissions.
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
The TCM controls the system and decides when to shift gears. It uses inputs from various sensors to determine when to shift gears for smooth driving and optimal fuel efficiency. This module makes the vehicle accelerate and decelerate properly.
Brake Control Module (BCM)
This ECU controls the braking system. It includes and traction control. The BCM gets data from speed sensors to prevent wheel lockup during hard braking and adjusts brake pressure as needed.
Body Control Module (BCM)
The BCM controls various electronic components in the vehicle’s body. It controls lights, windows, mirrors, and door locks. The BCM makes sure these work properly to increase safety and convenience for the driver and passengers.
Airbag Control Module (ACM)
The ACM monitors sensors around the vehicle to detect crashes. When it senses a big impact it decides which airbags to deploy and activates them to protect the passengers. The ACM gets data from crash sensors and seat sensors to make split-second decisions during an accident.
Climate Control Module (CCM)
The CCM controls the heating, ventilation and (HVAC) system in the vehicle. It adjusts fan speed, temperature and airflow to keep the interior comfortable. The CCM gets input from temperature sensors and user settings to optimize climate control.
Infotainment Control Unit (ICU)
The ICU manages the vehicle’s entertainment and information systems. It plays music, navigates routes and connects to smartphones via Bluetooth for hands-free calls. The ICU integrates with touchscreen displays, controls, and voice commands to make driving more enjoyable.
These ECUs work together to make vehicles run efficiently, safely, and comfortably. Each type does a specific job to make modern vehicles work.
References
- ECU (Electronic Control Unit) Explained. GoMechanic. Retrieved from on August 8, 2024
- What are the Different Types of Electronic Control Units?. LinkedIn. Retrieved from on August 8, 2024
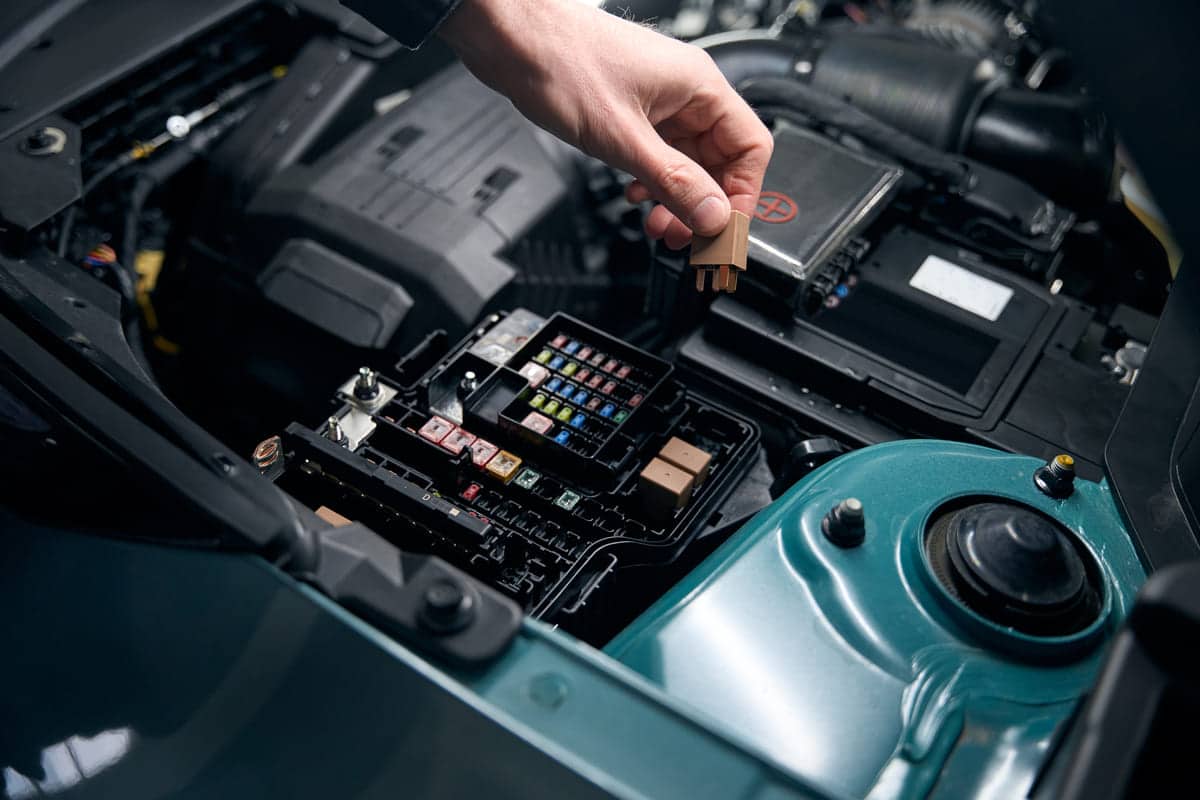

How Does An ECU Work?
Electronic control units (ECUs) are the brain of the vehicle. They make it run smoothly and safely by controlling different systems. Here’s how an ECU works:
Step 1: Get Data
The ECU gets data from various sensors in the vehicle. These sensors monitor engine temperature, speed and oxygen levels.
Step 2: Process
Once the ECU gets the data, it processes it using its internal software. The software makes decisions based on the pre-programmed instructions.
Step 3: Send Commands
After processing the data, the ECU sends commands to different parts of the vehicle. For example it may adjust or change ignition timing.
Step 4: Monitor
The ECU continuously monitors the outcome of its commands. It checks if the changes have improved performance and everything is working fine.
Step 5: Adjust
If the ECU finds any issues or deviations from optimal performance, it adjusts further. This continuous loop ensures efficiency and safety.
Step 6: Talk to other ECUs
In modern vehicles with multiple ECUs, these units talk to each other. They share data to coordinate functions like engine performance and braking.
Step 7: Store
The ECU stores data for later reference. Mechanics can access this data during diagnostics to troubleshoot issues.
By following these steps the ECU makes your vehicle run smoothly and efficiently, responding to real time conditions and driver inputs.
Electronic control units (ECUs) are like the brain of a vehicle. They help it run smoothly and safely by managing different systems. Here’s how an ECU works, step by step:
References
- ECU Explained. ECU Testing. Retrieved from on 08 August 2024
- What is an Electronic Control Unit? AutoPi. Retrieved from on 08 August 2024
Where is the ECU located in my car?
Finding the ECU in your can be tricky but it’s usually in predictable places. Here’s where you can find it:
- Under the Hood
- Under the
- Behind the Glove Box
- In the Center Console
- Near the Passenger Footwell
Different car manufacturers and models have the ECU in different places, so always check your vehicle’s manual for the exact location.
What are the components of the Electronic Control Module (ECM)?
Electronic Control Module (ECM) is the brain of your car’s engine. It has several key parts that help it control and manage engine functions. Here are the main parts:
- Microcontroller Unit (MCU)
- Memory
- Input Sensors
- Output Actuators
- Power Supply
- Communication Ports
These components work together to ensure your engine runs efficiently and smoothly.
References
- What is an Electronic Control Module (ECM)?. Cummins. Retrieved from on 08 August 2024
What Happens If My Car’s ECU Is Faulty?
A faulty ECU can cause many issues in your car as it controls various vehicle functions. Here’s what you may experience:
- Engine Performance Problems
- Warning Lights
- Poor Fuel Efficiency
- Transmission Issues
- Inconsistent Idling
- Electrical Component Failures
- Difficulty Diagnosing Issues
If you notice any of these signs, consult a professional mechanic to inspect and address the ECU.
References
- ECU in Car. Godigit. Retrieved from https://www.godigit.com/motor-insurance/car-insurance/car-parts/ecu-in-car. Retrieved on 08 August 2024