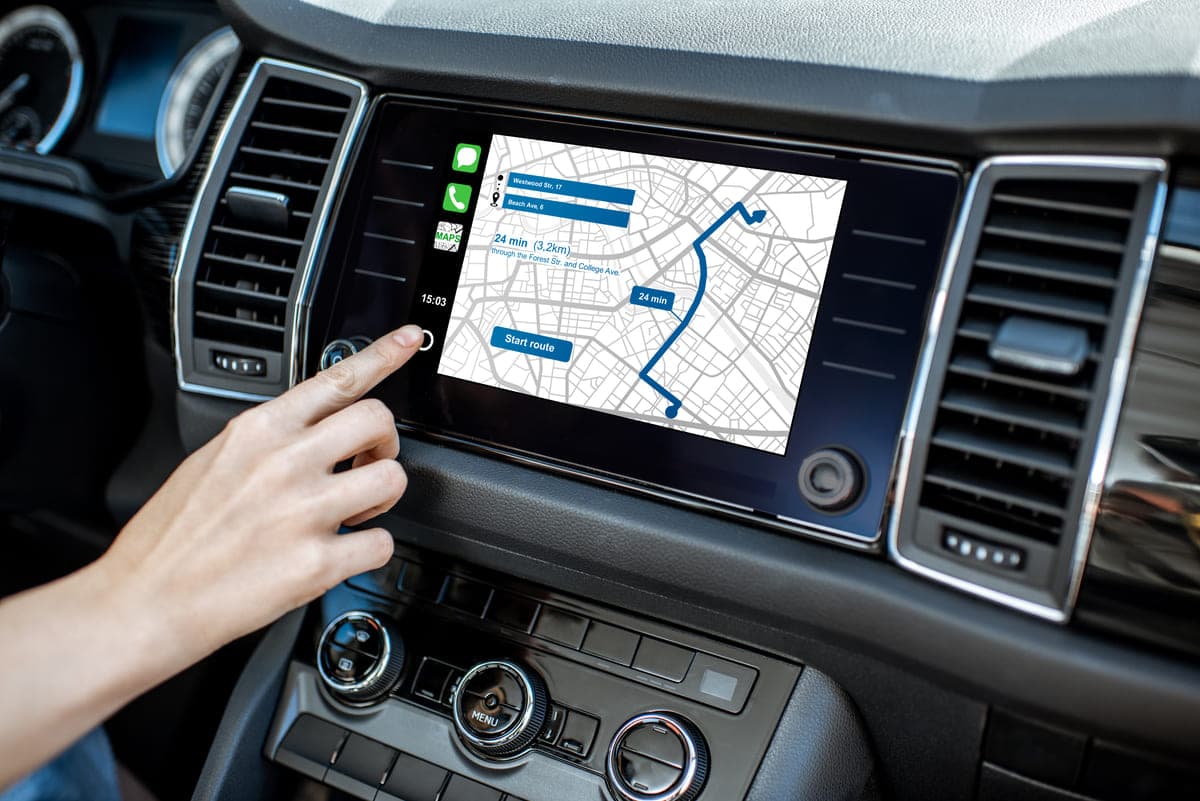
These systems leverage satellite technology and mapping data to offer turn-by-turn guidance, alert drivers to road conditions and suggest alternative routes. Designed for convenience and reliability, automotive navigation systems have become essential tools for modern-day driving and efficient travel.
Automotive navigation also known as navigation, uses GPS technology to provide directions. It helps drivers find the best routes to their destinations. These systems display maps and offer turn-by-turn guidance.
Drivers can input destinations using touchscreens or voice commands. The system calculates the optimal route based on real-time traffic data. It may also provide points of interest like gas stations and restaurants.
Some systems offer additional features. These include real-time traffic updates, speed limit alerts, and lane guidance. These features enhance safety and efficiency for drivers.
Automotive navigation systems are now standard in many vehicles. They have transformed modern driving experiences.
References
- Automotive navigation system. Wikipedia. Retrieved from
- Automotive Navigation System. Digit. Retrieved from
Car navigation systems have evolved significantly since the 1980s. The Etak Navigator, introduced in 1985, was one of the first car navigation systems. It used digital maps on cassette tapes and magnetic sensors to track the vehicle’s position.
In the 1990s, GPS technology became more widespread and affordable. This led to more accurate and user-friendly navigation systems in cars. Luxury brands like BMW and Toyota were among the first to incorporate GPS-based navigation into their vehicles.
Portable GPS devices gained popularity in the early 2000s. Companies such as Garmin and TomTom produced these devices, providing an alternative to built-in systems. These portable units offered easy installation and regular updates, making them a popular choice for many drivers.
Today, integrated navigation systems are standard in most new cars. Modern systems use real-time traffic data, internet connectivity, and advanced mapping technologies. These features provide drivers with up-to-date information and efficient route planning.
References
- History of Automotive Navigation Systems. Wikipedia. Retrieved from
- 1981 Navigation System. Honda Global. Retrieved from
Here are the detailed workings of a car navigation system:
- Receive GPS Signals: The system starts by receiving signals from multiple GPS satellites. These signals determine the vehicle’s exact location.
- Input Destination: The driver inputs the desired destination using a touchscreen, buttons, or voice commands. This step sets the target for the navigation system.
- Calculate Route: The system calculates the optimal route to the destination. It considers factors like distance, road types, and traffic conditions.
- Display Map: The calculated route appears on a digital map. The display shows the path that the vehicle should follow.
- Provide Directions: The system gives turn-by-turn directions through prompts and visual cues. This helps the driver navigate without needing to constantly check the map.
- Continuous Update: As the vehicle moves, the system continuously updates its position using GPS data. This ensures the directions remain accurate throughout the journey.
- Real-Time Traffic Data: Modern systems receive real-time traffic updates. They can suggest alternate routes to avoid congestion or roadblocks.
- Additional Features: Some systems offer additional features like speed limit alerts, lane guidance, and points of interest. These features enhance the overall driving experience.
- Integration with Other Systems: Many car navigation systems integrate with smartphones and other car features. This allows for hands-free calling, media playback, and more.
These steps outline the basic operation of a car navigation system, providing efficient and reliable guidance for drivers.
References
- GPS Navigation System. NASA Space Place. Retrieved from
- How GPS Works. Federal Aviation Administration. Retrieved from
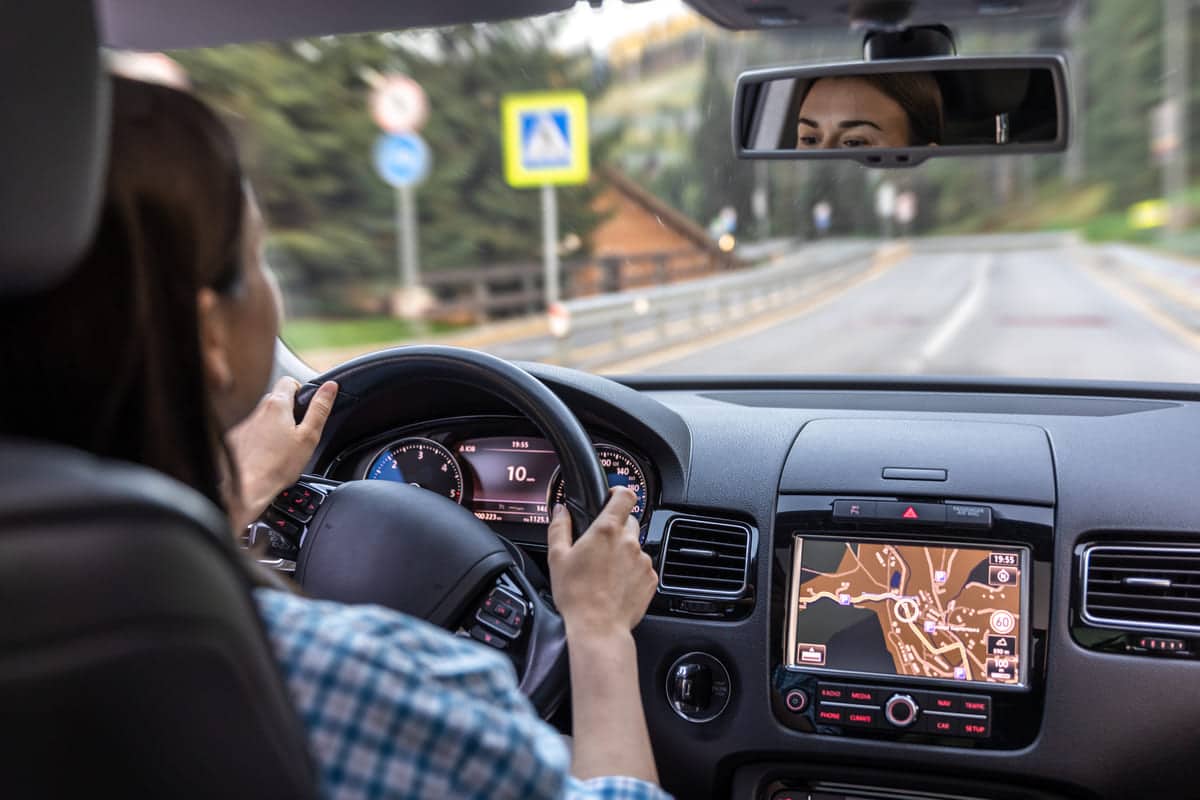

Car navigation systems offer several key features to enhance driving. These include:
- Turn-by-Turn Directions: The system provides clear audio and visual directions for every turn. This helps drivers navigate routes easily.
- Real-Time Traffic Updates: The system receives live traffic information. It suggests alternate routes to avoid congestion and roadblocks.
- Points of Interest: The system highlights nearby locations like gas stations, restaurants, and hotels. This makes it easier for drivers to find essential services on the go.
- Voice Commands: Drivers can use voice commands to input destinations and control the system. This feature promotes safer, hands-free operation.
- Lane Guidance: The system advises which lane to use for upcoming turns or exits. This feature helps prevent last-minute lane changes.
- Speed Limit Alerts: The system shows current speed limits and provides alerts if the driver exceeds them. This helps promote safe driving.
- Map Updates: Many systems offer regular map updates. This ensures that the navigation data remains current and reliable.
- Integration with Smartphones: The system can connect to smartphones via Bluetooth or USB. This allows for hands-free calls, message reading, and music streaming.
- 3D Maps and Landmarks: Some systems display 3D maps and landmarks for better orientation. This feature enhances the visual experience for drivers.
These features collectively contribute to a comprehensive and user-friendly car navigation experience.
References
- Internal Combustion Engines. ScienceDirect. Retrieved from
- In-vehicle Navigation Systems: Interface Characteristics and Industry Trends. ResearchGate. Retrieved from
- Overview of Automotive Navigation Systems: Features, Market, and Future. IoT Insider. Retrieved from
Automotive navigation systems come in several types. These include:
- Built-In Systems: Manufacturers install these systems directly into the vehicle’s . They integrate with the car’s other features, providing a seamless experience.
- Portable GPS Devices: Drivers can easily move these standalone units between vehicles. Brands like Garmin and TomTom produce these popular devices.
- Smartphone-Based Systems: Apps like Google Maps and Apple Maps turn smartphones into navigation tools. Drivers mount their phones on the dashboard for easy viewing.
- Aftermarket Systems: These systems are installed after purchasing the vehicle. They can replace or supplement the factory-installed navigation system.
- Hybrid Systems: These combine built-in systems with smartphone connectivity. They offer features from both types, providing enhanced functionality.
These types cater to different needs and preferences, offering various options for automotive navigation.
References
- Automotive Navigation System. Simple English Wikipedia. Retrieved from
- Which Type of Car Navigation System Is Best?. Consumer Reports. Retrieved from https://www.consumerreports.org/cars/automotive-technology/which-type-of-car-navigation-system-is-best-a1197279757/