Automotive fuses are the guardians of the vehicle’s electrical system. They interrupt the current flow when it gets excessive and prevent wiring and component damage. Each fuse is designed for the specific electrical load so it’s reliable and safer.
What is an Automotive Fuse?
An automotive fuse also known as a fuse, automobile fuse, and vehicle fuse is a small replaceable part in the vehicle electrical system. It protects the circuits from overcurrent and short circuits. When current exceeds the safe level the fuse blows and breaks the circuit.
Fuses come in different types and ratings, each for a specific electrical load. Blade fuses are common in modern vehicles while older cars use glass tube fuses.
Replacing a blown fuse is easy. Find the vehicle’s fuse box, locate the blown fuse using the diagram, and replace it with one of the same amperage rating. Proper maintenance is key to safety and functionality.
References
- Automotive fuse. Wikipedia. Retrieved from
What Are Different Types of Automotive Fuses?
There are several types of automotive fuses, each for specific use. Knowing these types is important for maintenance and repair.
- Blade Fuses:Blade fuses are the most common in modern vehicles. It has a plastic body with two metal prongs that fit into the fuse box.
- Glass Tube Fuses: Glass tube fuses are found in older vehicles. It has a glass cylinder with a metal filament inside, visible when blown.
- Ceramic Fuses: Ceramic fuses can handle higher temperatures and currents. Used in heavy-duty applications where extra protection is needed.
- Mini and Micro Blade Fuses: Mini and micro-blade fuses are smaller versions of standard-blade fuses. They save space in compact fuse boxes but provide similar protection.
- Maxi Fuses: Maxi fuses are big and high-current fuses used in main power distribution areas. They protect circuits with heavy electrical loads like those in trucks and SUVs.
References
- Blade type. Wikipedia. Retrieved from
How Does an Automotive Fuse Work?
An automotive fuse protects the vehicle’s electrical system from overcurrent. Here’s how it works:
- Current Flow: Electrical current flows through the fuse’s metal filament, connecting the circuit.
- Overcurrent Detection: If the current exceeds the fuse’s rated capacity, the filament gets hot.
- Filament Melting: The excessive heat melts the filament and breaks the connection.
- Circuit Interruption: The broken filament interrupts the current flow and stops the current from passing through.
- Protection: This interruption protects the vehicle wiring and electronic components from damage. Replacing the blown fuse restores the circuit functionality.
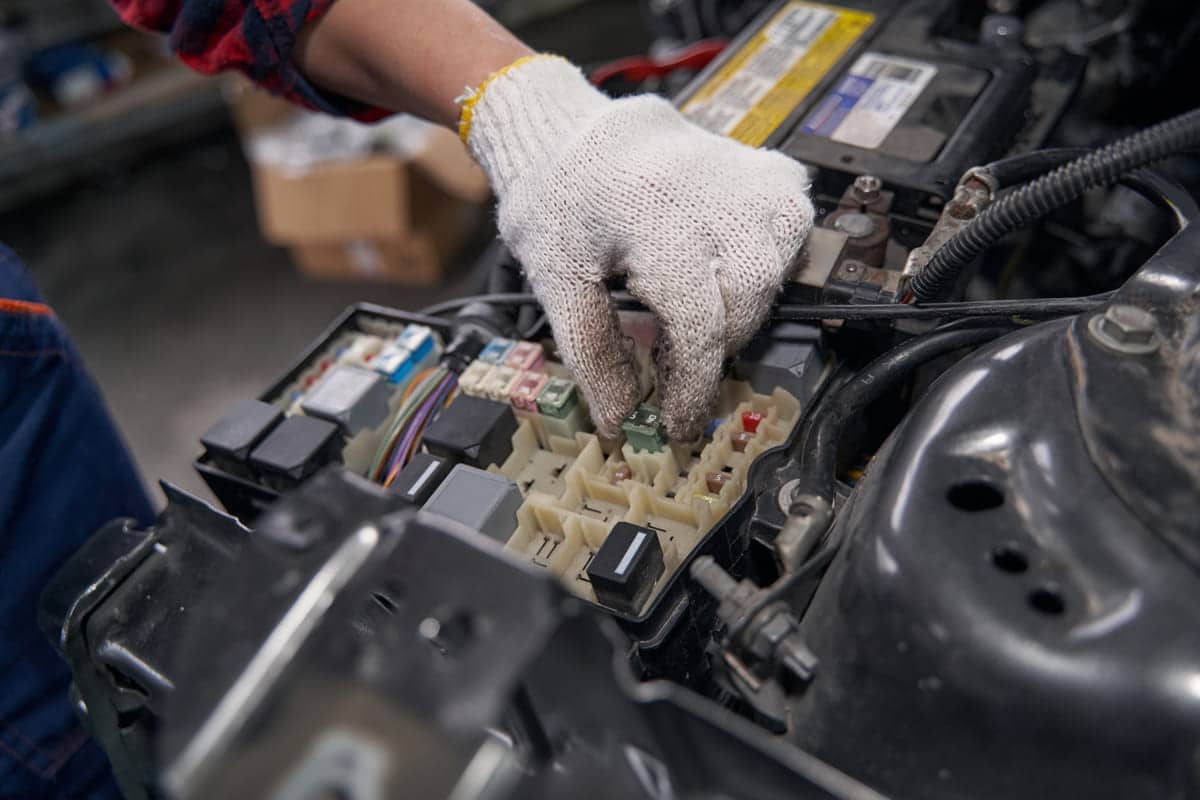
Where is the Automotive Fuse Box Located?
The automotive fuse box contains all the motor vehicle fuses. Location varies by make and model.
Usually you will find the main fuse box under the on the driver’s side. It may be behind a panel or cover for protection.
Another common location is inside the compartment. Look near the or along the firewall for a black box with a fuse label.
Check your vehicle’s service manual for the exact location. The manual has diagrams and instructions on how to access the fuse boxes. Knowing these locations will help you to quickly check and replace the fuses.
References
- Identifying Automotive Fuse Types. SWE-Check. Retrieved from
How To Change the Vehicle Fuse?
Changing a car fuse is easy. Follow these steps:
- Locate the Fuse Box: Check your vehicle’s manual to find the fuse box. Common locations are under the dashboard and in the engine compartment.
- Identify the Blown Fuse: Use the diagram on the fuse box cover or in the manual to find the blown fuse. A blown fuse has a broken metal filament.
- Remove the Blown Fuse: Use a fuse puller or needle-nose pliers to carefully pull out the blown fuse from its slot.
- Find a Replacement: Match the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. The rating is printed on the fuse.
- Insert the New Fuse: Push the new fuse into the slot until it clicks. Make sure it’s seated properly.
- Test the Circuit: Turn on the vehicle and test the circuit that had the blown fuse. Make sure everything is working before closing the fuse box.
- Close the Fuse Box: Replace any covers or panels you removed. Make sure everything is back in place for protection.
References
- Car Fuses Guide. RS Components. Retrieved from https://uk.rs-online.com/web/content/discovery/ideas-and-advice/car-fuses-guide


